There are six types of play in volleyball. They are as follows.
- Service
- Reception (serve-receive)
- Set
- Attack
- Dig
- Block
Of the above six plays, there is one spectacular play in particular that never ceases to fascinate all volleyball players. It is the attack. It is a well-known fact that the number of points scored in an attack has a huge impact on the outcome of a match. And the skill most often used in attack play is the spike. That is the spike.
In this article, we will focus on the spike swing and explore it in depth.
Three categories of spike swings
The spike swing can be classified into three main categories. They are as follows.
- circular arm swing
- bow and arrow arm swing
- straight arm swing
- circular arm swing (hereafter ‘circular’)
The circular arm swing is named after the circular trajectory of the elbow. The main feature of this form is that the take-back is completed quickly and a large amount of power can be generated in a short period of time. Power is mainly generated by the trunk rotation and lateral bending movements.
- bow and arrow arm swing (hereafter ‘ bow and arrow’)
Named because the form is reminiscent of the action of drawing a bow and arrow. Compared to the circular, it takes longer to complete the take-back and requires more time to prepare to generate greater power. Power is generated mainly through trunk rotation and back and forth flexion. 3.
- straight arm swing (hereafter ‘ straight’)
Named after the straight arm swing, in which the arm is swung straight down to hit. The take-back is small and the swing is compact, so power is unlikely to be generated. Power is generated mainly by the backbending and forward bending movements of the trunk.
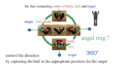
Trunk rotation, lateral flexion and back and forth flexion
Having given an overview of the three categories of the spike swing, we will now explain the movements of the trunk, which are considered important in deepening the understanding of each swinging movement. First, please see the diagram below.
There are three main types of trunk movement. They are rotation, lateral flexion and anterior/posterior flexion.
“Rotation” refers to rotation of the body axis to the left or right, with rotation to the left being referred to as left rotation and rotation to the right being referred to as right rotation.
“Lateral flexion” refers to bending the body axis to the left or right side; bending to the left side is called left lateral flexion and bending to the right side is called right lateral flexion.
“Anterior/posterior bending” refers to bending the body axis backwards and forwards. Forward bending is called forward bending and backward bending is called backward bending.
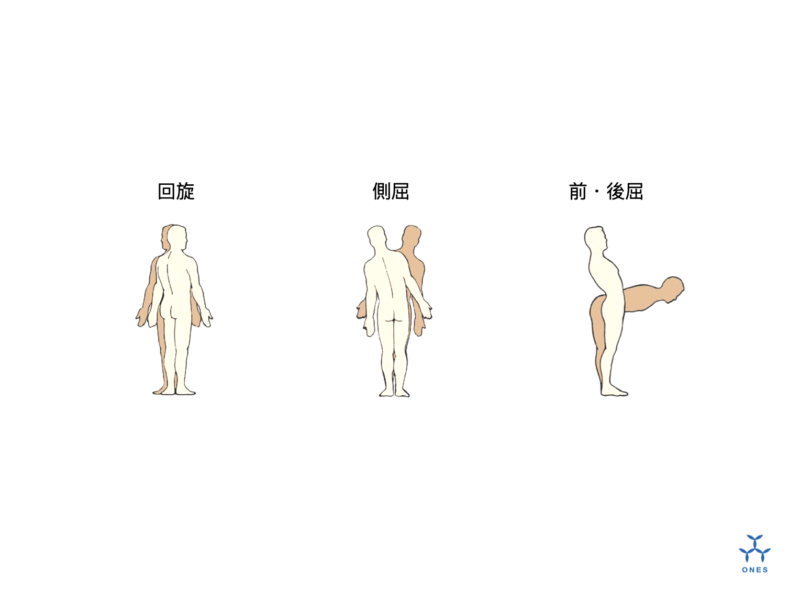
Zero position
Next, an explanation of the zero position, which is essential when considering the spike swing action, is also worth mentioning.
The zero position refers to the ideal position (position) to hit the ball in the volleyball spike swing. The advantages of hitting the ball in the zero position and the origin of the name are as follows.
- Zero muscle tension in the inner muscles around the spike shoulder joint (shoulder joint is stable).
- The point at which there is zero twisting stress on the humerus, such as external or internal rotation (most de-energised)
- The angle between the humerus and scapula is zero (0) degrees.
The following section will explain in detail the principle of operation of each spike swing, together with a series of photographs.